Facilities and Equipment
Facilities, technology and equipment for the Human Performance and Biodynamics Lab (HPB Lab) are shared between WSSU School of Health Sciences and WFU School of Medicine per a collaborative agreement between the educational institutions. The HPB Lab is located in the Piedmont Plaza 1 building- a facility operated by Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist, the clinical enterprise that partners with WFU School of Medicine.
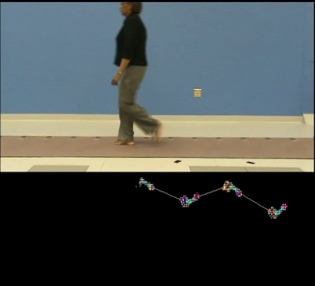
With over 2000 square feet of laboratory space and a 12-foot high ceiling, the HPB Lab has a substantial amount of room for teaching, clinical, and research purposes. The center of the lab features an approximately 30-foot walking track surrounded by 3D motion capture cameras, where many data collections are performed for both clinical and research purposes. The space also includes office space with computers for lab staff and student use, and a changing room for patients/research participants.
The Human Performance and Biodynamics Lab's cutting-edge technology and state-of-the-art equipment provides researchers and clinicians the ability to perform a variety of both qualitative and quantitative movement analysis studies. These comprehensive, evidence-based analyses have proven to be beneficial in helping to identify underlying causes for movement abnormalities in pathologic patient groups, such as individuals with knee osteoarthritis or cerebral palsy. This type of work can also help to determine if surgery and/or physical therapy may be necessary for improving specific movement characteristics over time, and to what extent, based on scientific data collected in the lab.
- 10-Camera Motion Capture System (Motion Analysis Corp.)
- 4 Floor-Embedded Force Platforms (AMTI, Inc.)
- Visual 3D Modeling/Analysis Software (C-Motion, Inc.)
The HPB Lab's 3D motion capture system consists of 10 infrared cameras and analysis software to record, track, and analyze complex movements with extreme accuracy. These real-time cameras track reflections from spherical markers attached to various anatomical locations on the body. Four force platforms embedded into the floor are used to measure the amount of force that is applied to the ground during a particular movement. With data collected from the cameras and force platforms, we are able to build a 3D skeletal model representation of the human body, and calculate joint motion, forces, and moments for a variety of movements including walking, running, throwing, jumping, kicking and swinging. Outcome measures provided by using a motion capture system have been shown to be useful in evaluating movement limitations and/or proficiencies, and determining the best course of treatment protocols in various patient populations.
- GAITRite® Platinum Plus Classic Walkway (CIR Systems, Inc.)
The standard GAITRite® electronic walkway provides a simple way to obtain valid, reliable, and objective spatiotemporal measures of gait, in real-time. As a patient ambulates across the walkway, the software records pressure data, capturing the geometry and relative arrangement of each footfall as a function of time and space. This software provides various spatiotemporal gait parameters such as gait velocity, stride length, step length, cadence, single/double support time, and much more! The walkway is portable and requires minimal setup and test time, making it very useful for a quick gait analysis in either the lab, classroom or even clinical setting.
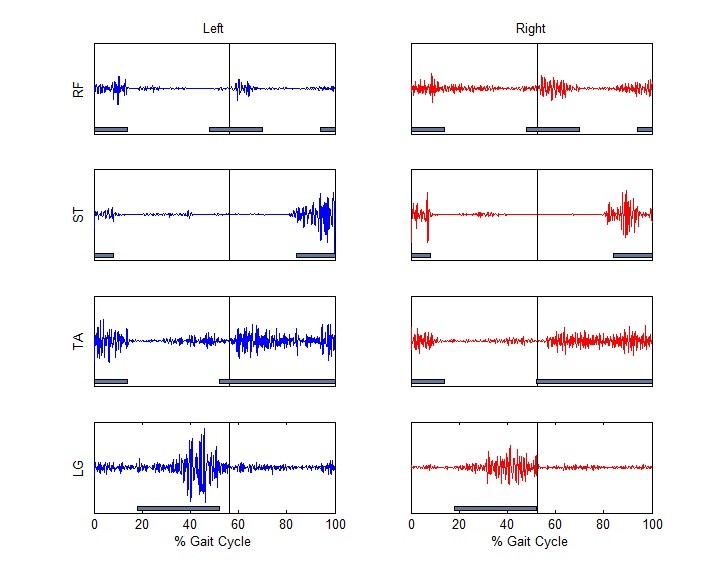
- Noraxon® Ultium® EMG System with 8 Wireless Surface EMG + IMU Sensors (Noraxon® USA, Inc.)
Electromyography (EMG), is described as an experimental technique describing the neuromuscular activation of muscles within postural tasks, functional movements, work conditions and treatment/training regimes. A variety of disciplines use EMG to provide insights into how we perform movement which include: biomechanists, physical therapist, clinicians, and strength coaches. Participants perform movement tasks while neuromuscular activity is recorded. This work provides us with the basic knowledge of how motor units are recruited in certain musculature for a given movement task. The completely wireless EMG equipment is used to measure the activation of individual muscles, but also has accelerometry capabilities. These data can be used in combination with the camera and force plate data to account for muscle co-contraction (agonist and antagonist muscles activated simultaneously).
- HUMAC® NORM™ Isokinetic Dynamometer (CSMI, Inc.)
Designed to be adaptable to patient needs as well as a clinician/researcher's own treatment methods and ideas, this dynamometer system provides anatomically correct positioning and positive stabilization for testing of the musculature surrounding the shoulder, elbow, forearm, wrist, ankle, knee and hip. NORM™ isolated-joint testing and rehabilitation systems have proven extremely valuable for quantification and rehabilitation of physical impairment. Additionally, they have been used in clinical research and for gathering human performance data. In physical therapy, strength dynamometer systems are often used to exercise, measure, evaluate, and increase the strength and control of muscles, and increase the Range of Motion (ROM) of joints.

- Novel Pressure Distribution Measurement Systems (pedar®, emed®, pliance®)
- Scientific Analysis Software (Novel Electronics, Inc.)

Novel pressure distribution measurement systems allow for the measurement and analysis of the amount of pressure that is applied across a given source of application or surface, such as various regions of the foot or hand. The pedar® system provides the ability to capture dynamic in-shoe pressures, revealing the interaction between footwear and the foot. The emed® system measures barefoot pressures without the influence of footwear, while walking across a stationary platform. The pliance® system analyzes the distribution of pressure when applied on varying surfaces such as a wheelchair seat or a residual limb. Common applications for pressure distribution measurement systems include: screening for disorders secondary to diabetes or other neuropathic issues, observation of movement disabilities, regulation of weight bearing activity following surgery. Other applications may also involve tissue pressures while sitting, standing, rolling or performing other functional activities.
- NeuroCom® SMART Balance Master® System (Natus Medical, Inc.)

A NeuroCom® system can be used to evaluate the contributions of the vestibular, visual, and proprioceptive systems on balance control. This system's software includes standardized tests of sensory organization, limits of stability, dynamic visual acuity, and more! Additional force plate equipment allows for interactive, functional training exercises using visual biofeedback, coupled with sensitive, real-time monitoring of movement. These assessments and training protocols help to motivate patients or research participants to achieve greater balance control faster.

A virtual reality system uses a green screen to allow children to see themselves immersed in a video game, as they participate in interactive activities and games with underlying focus on movement and balance. This technology often helps to reduce discomfort and increase compliance during rehabilitation.
A collaboration between Wake Forest University School of Medicine and Winston-Salem State University School of Health Sciences
